Because the EU Council heads to vote on the so-called “Chat Management” regulation, Germany might show the deciding issue.
Put ahead by Denmark, the regulation would basically eradicate encrypted messaging, requiring providers reminiscent of Telegram, WhatsApp and Sign to permit regulators to display messages earlier than they’re encrypted and despatched.
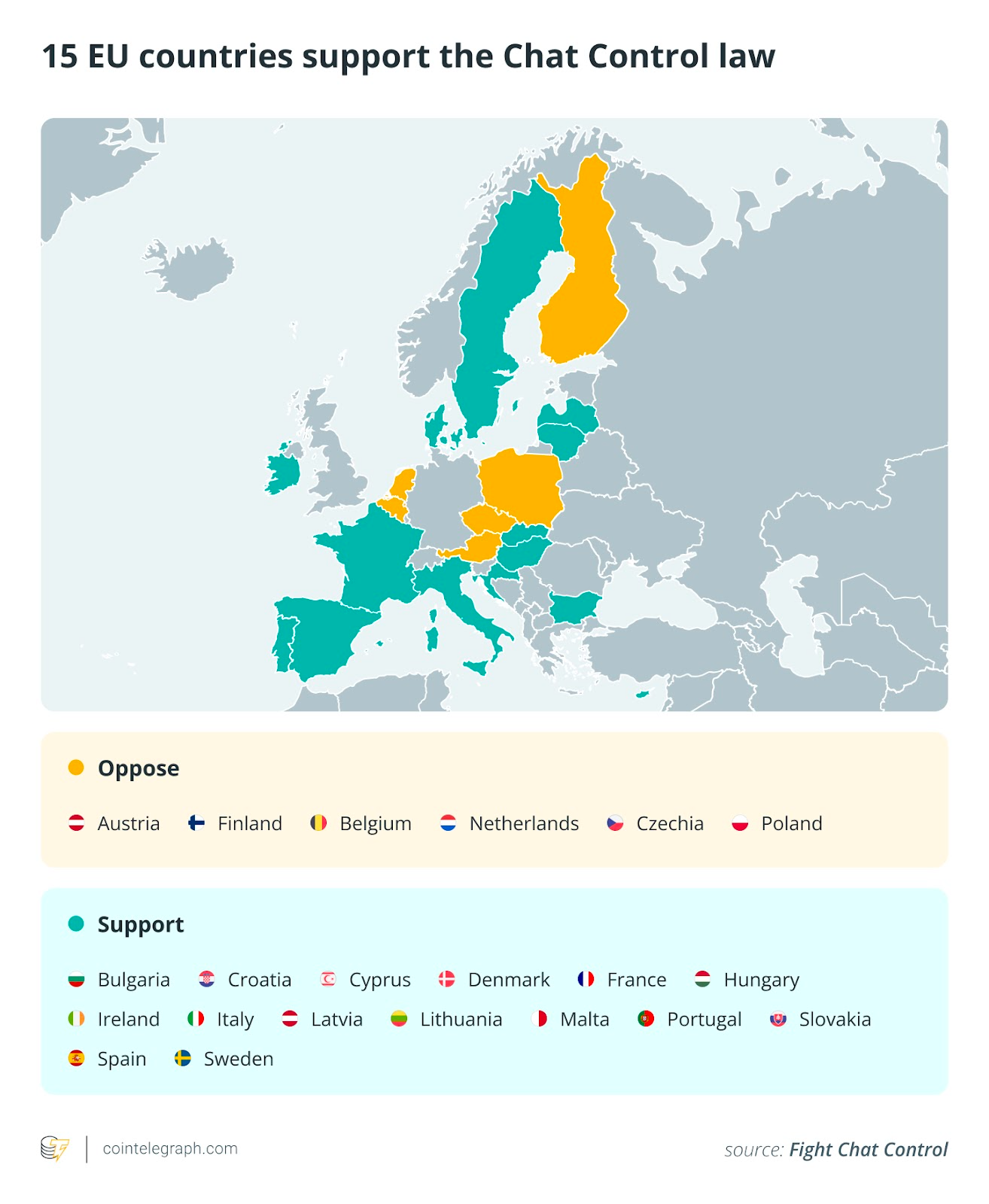
Legislators from 15 member states of the EU have indicated assist for the invoice, however these nations don’t represent not less than 65% of the EU inhabitants, which means they want extra assist.
Germany has been on the fence about supporting the regulation, and it might deal a serious blow to privateness in Europe if it decides to assist it.
EU Chat Management invoice goals to struggle youngster abuse
The Regulation to Stop and Fight Baby Sexual Abuse (CSA), or “Chat Management” regulation, was first launched by then-European Commissioner for House Affairs Ylva Johansson in 2022. It goals to struggle the unfold of on-line youngster sexual abuse materials (CSAM) by way of, amongst different issues, screening messages earlier than they’re encrypted. The regulation has beforehand failed to realize the assist vital to maneuver ahead.
On July 1, the primary day of Denmark’s presidency of the Council of the European Union (EU Council), the nation mentioned the directive would obtain “excessive precedence.”
For the reason that starting of Denmark’s six-month presidency of the council, member states have been solidifying their positions, which they’re anticipated to finalize earlier than a gathering on Sept. 12 and an eventual vote on Oct. 14.
The supporting block wants extra assist to comprise 65% of the EU inhabitants and acquire a professional majority. Six nations stay undecided, in keeping with Battle Chat Management, an activist group against the regulation:
-
Estonia
-
Germany
-
Greece
-
Luxembourg
-
Romania
-
Slovenia.
Amongst these nations, Germany is important to sway the result of the EU Council vote. Its 83 million residents would convey the inhabitants of nations supporting Chat Management to some 322 million, or 71% of the EU. The opposite 5 nations mixed, even when they voted in assist, don’t make up a big sufficient phase of the inhabitants.
Associated: EU proposal to scan all non-public messages good points momentum
Per Battle Chat Management, many German members of the European Parliament (MEPs) oppose the draft regulation. Citing paperwork from a July 11 assembly leaked to German publication Netzpolitik.org, it discovered opposition to Chat Management throughout the political spectrum. MEPs from the Bündnis 90/Die Grünen and Various für Deutschland — respectively representing the center-left and far-right of German opposition politics — oppose Chat Management.
Nonetheless, an equally massive variety of parliamentarians from the ruling Social Democrats, Christian Democrats and Social Democratic Union of Bavaria are reportedly uncommitted.
Some are involved that these uncommitted lawmakers may very well be inclined to take current German regulation and apply it to the whole EU.
Germany already has legal guidelines that enable police to avoid encryption utilized by well-liked messaging platforms like WhatsApp and Sign. In 2021, the Bundestag amended legal guidelines to permit the police to intercept communications of “individuals in opposition to whom no suspicion of a criminal offense has but been established and due to this fact no prison process measure can but be ordered.”
Software program developer and privateness rights advocate Jikra Knesl mentioned, “A type of ChatControl already exists in Germany. Corporations like Meta are sharing their experiences with the police.”
If expanded to the whole EU, it might have an effect on “hundreds of thousands of harmless folks whose properties is perhaps searched even after they did nothing incorrect,” he mentioned.
Civil society mobilizes in opposition to Chat Management
As the choice attracts nearer, civil rights teams, activists and even European parliamentarians have been talking out in opposition to Chat Management.
Emmanouil Fragkos, an MEP for the right-wing Greek Resolution occasion, submitted a parliamentary query about Chat Management in July. He mentioned {that a} evaluation of the regulation “raised new, grave issues concerning the respect of elementary rights within the EU.”

Oliver Laas, a junior lecturer of philosophy at Tallinn College, wrote in an op-ed on Monday that legal guidelines like Chat Management “are laying the groundwork within the current for a possible democratic backslide.”
“In a world that’s slowly however certainly turning into extra authoritarian, people usually are not protected by the state’s surveillance capabilities being reined in by regulation — they’re protected by the absence of such capabilities altogether,” he mentioned.
One other level of competition is the affect Chat Management might have on the efficacy of encryption know-how.
Fragkos mentioned that creating obligatory gaps in encryption would “create safety gaps open to exploitation by cybercriminals, rival states and terrorist organisations.”
The FZI Analysis Middle for Data Know-how, a nonprofit group for IT analysis, launched a place paper opposing Chat Management final 12 months. It acknowledged that the objective of the regulation is undisputed, however Chat Management’s implementation would each weaken consumer rights to privateness and the efficacy of encryption know-how itself.
Sascha Mann, coverage shaper for digitalization and digital rights at Volt Europa — a federalist, pan-European political occasion within the European Parliament — additionally questioned the efficacy of Chat Management.
“Moreover the problems of privateness and consent, chat management could even hinder regulation enforcement efforts to successfully struggle sexual abuse,” he mentioned. The sheer quantity of content material despatched by messengers within the EU would “end in an abundance of false positives that might eat up regulation enforcement sources.”
Some 400 scientists from international analysis establishments confirmed this downside of false positives in an open letter signed this morning.
“Current analysis confirms that state-of-the-art detectors would yield unacceptably excessive false constructive and false damaging charges, making them unsuitable for large-scale detection campaigns on the scale of a whole bunch of hundreds of thousands of customers as required by the proposed regulation,” the letter learn.
Mann advised it might be higher for the EU to implement options advised by organizations combating CSA. These included deleting CSA supplies on-line after an investigation and growing regulation enforcement sources.
On Friday, Europe will see whether or not these issues are sufficient to persuade undecided MEPs and chart the long run for digital privateness, or lack thereof, within the EU.
Journal: Can Robinhood or Kraken’s tokenized shares ever be actually decentralized?