Menace actors have discovered a brand new strategy to ship malicious software program, instructions, and hyperlinks inside Ethereum good contracts to evade safety scans as assaults utilizing code repositories evolve.
Cybersecurity researchers at digital asset compliance agency ReversingLabs have discovered new items of open-source malware found on the Node Bundle Supervisor (NPM) bundle repository, a big assortment of JavaScript packages and libraries.
The malware packages “make use of a novel and inventive method for loading malware on compromised gadgets — good contracts for the Ethereum blockchain,” ReversingLabs researcher Lucija Valentić mentioned in a weblog publish on Wednesday.
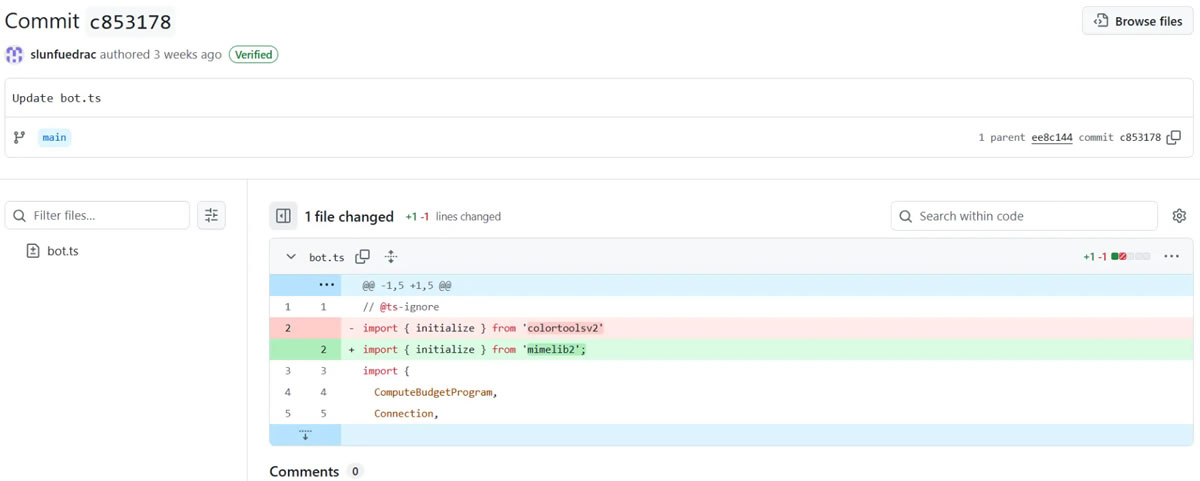
The 2 packages, “colortoolsv2” and “mimelib2,” printed in July, “abused good contracts to hide malicious instructions that put in downloader malware on compromised programs,” defined Valentić.
To keep away from safety scans, the packages functioned as easy downloaders and as a substitute of instantly internet hosting malicious hyperlinks, they retrieved command and management server addresses from the good contracts.
When put in, the packages would question the blockchain to fetch URLs for downloading second-stage malware, which carries the payload or motion, making detection harder since blockchain site visitors seems professional.
A brand new assault vector
Malware focusing on Ethereum good contracts isn’t new; it was used earlier this 12 months by the North Korean-affiliated hacking collective the Lazarus Group.
“What’s new and totally different is the usage of Ethereum good contracts to host the URLs the place malicious instructions are positioned, downloading the second-stage malware,” mentioned Valentić, who added:
“That’s one thing we haven’t seen beforehand, and it highlights the quick evolution of detection evasion methods by malicious actors who’re trolling open supply repositories and builders.”
An elaborate crypto deception marketing campaign
The malware packages had been half of a bigger, elaborate social engineering and deception marketing campaign primarily working via GitHub.
Menace actors created faux cryptocurrency buying and selling bot repositories designed to look extremely reliable via fabricated commits, faux consumer accounts created particularly to observe repositories, a number of maintainer accounts to simulate energetic improvement, and professional-looking venture descriptions and documentation.
Associated: Crypto customers warned as adverts push malware-laden crypto apps
Menace actors are evolving
In 2024, safety researchers documented 23 crypto-related malicious campaigns on open-source repositories, however this newest assault vector “reveals that assaults on repositories are evolving,” combining blockchain know-how with elaborate social engineering to bypass conventional detection strategies, Valentić concluded.
These assaults usually are not solely executed on Ethereum. In April, a faux GitHub repository posing as a Solana buying and selling bot was used to distribute obscured malware that stole crypto pockets credentials. Hackers have additionally focused “Bitcoinlib,” an open-source Python library designed to make Bitcoin improvement simpler.
Journal: Bitcoin to see ‘another large thrust’ to $150K, ETH stress builds: Commerce Secrets and techniques