- NZD/USD surges to close 0.5930 because the market sentiment turns favorable for riskier property.
- Delicate US NFP information for August has prompted Fed dovish hypothesis.
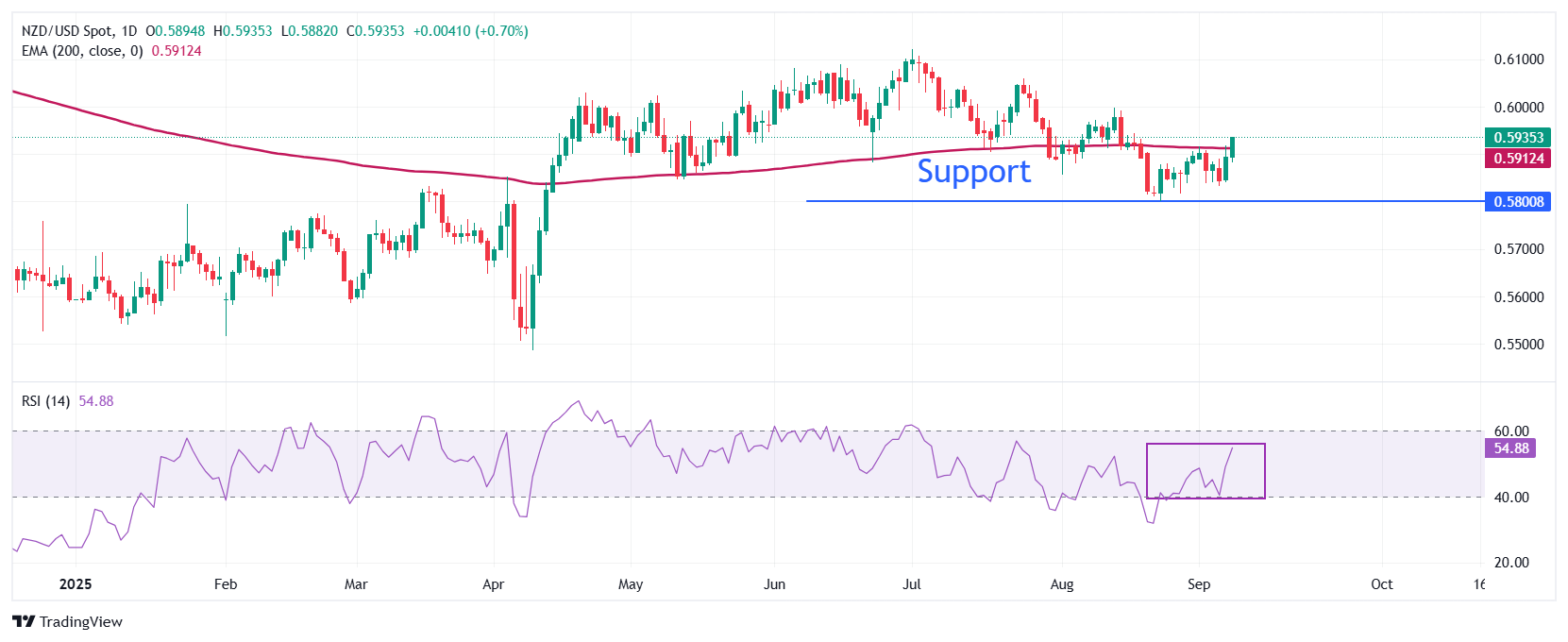
- NZD/USD breaks above the 200-day EMA, which trades round 0.5912.
The NZD/USD pair trades 0.66% larger to close 0.5930 in the course of the European buying and selling session on Monday. The Kiwi pair strengthens because the New Zealand Greenback (NZD) outperforms its friends amid cheerful market sentiment.
New Zealand Greenback Value In the present day
The desk under reveals the share change of New Zealand Greenback (NZD) towards listed main currencies in the present day. New Zealand Greenback was the strongest towards the US Greenback.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.15% | -0.20% | -0.35% | -0.23% | -0.61% | -0.72% | -0.38% | |
| EUR | 0.15% | -0.06% | -0.12% | -0.09% | -0.45% | -0.51% | -0.23% | |
| GBP | 0.20% | 0.06% | -0.16% | -0.00% | -0.38% | -0.47% | -0.17% | |
| JPY | 0.35% | 0.12% | 0.16% | 0.05% | -0.28% | -0.52% | -0.00% | |
| CAD | 0.23% | 0.09% | 0.00% | -0.05% | -0.29% | -0.44% | -0.15% | |
| AUD | 0.61% | 0.45% | 0.38% | 0.28% | 0.29% | -0.08% | 0.22% | |
| NZD | 0.72% | 0.51% | 0.47% | 0.52% | 0.44% | 0.08% | 0.30% | |
| CHF | 0.38% | 0.23% | 0.17% | 0.00% | 0.15% | -0.22% | -0.30% |
The warmth map reveals share adjustments of main currencies towards one another. The bottom foreign money is picked from the left column, whereas the quote foreign money is picked from the highest row. For instance, if you happen to choose the New Zealand Greenback from the left column and transfer alongside the horizontal line to the US Greenback, the share change displayed within the field will symbolize NZD (base)/USD (quote).
The demand for riskier property has elevated because the Federal Reserve (Fed) appears sure to chop rates of interest within the financial coverage announcement subsequent week.
Based on the CME FedWatch instrument, merchants see a ten% likelihood that the Fed will reduce rates of interest by 50 foundation factors (bps) to three.75%-4.00%, whereas the remainder level a 25-bps rate of interest discount.
Fed dovish hypothesis has intensified as a result of cooling United States (US) labor market situations.
Upbeat market sentiment has dampened the safe-haven attraction of the US Greenback (USD). Throughout the press time, the US Greenback Index (DXY), which tracks the Buck’s worth towards six main currencies, trades decrease to close 97.60.
NZD/USD extends its upside above the 200-day Exponential Shifting Common (EMA), which trades round 0.5912.
The 14-day Relative Power Index (RSI) approaches 60.00. A recent bullish momentum would emerge if the RSI breaks above that stage.
Going ahead, the Kiwi pair would rise in direction of the June 19 excessive of 0.6040 and the September 11 low of 0.6100 if it manages to return above the psychological stage of 0.6000.
In an alternate state of affairs, a draw back transfer by the pair under the August 2 low of 0.5800 will expose it to the April 11 low of 0.5730, adopted by the round-level help of 0.5700.
NZD/USD each day chart
US Greenback FAQs
The US Greenback (USD) is the official foreign money of the USA of America, and the ‘de facto’ foreign money of a major variety of different nations the place it’s present in circulation alongside native notes. It’s the most closely traded foreign money on the planet, accounting for over 88% of all world overseas change turnover, or a median of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, in accordance with information from 2022.
Following the second world struggle, the USD took over from the British Pound because the world’s reserve foreign money. For many of its historical past, the US Greenback was backed by Gold, till the Bretton Woods Settlement in 1971 when the Gold Normal went away.
Crucial single issue impacting on the worth of the US Greenback is financial coverage, which is formed by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to realize worth stability (management inflation) and foster full employment. Its main instrument to realize these two targets is by adjusting rates of interest.
When costs are rising too rapidly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% goal, the Fed will increase charges, which helps the USD worth. When inflation falls under 2% or the Unemployment Charge is just too excessive, the Fed might decrease rates of interest, which weighs on the Buck.
In excessive conditions, the Federal Reserve may print extra {Dollars} and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the method by which the Fed considerably will increase the movement of credit score in a caught monetary system.
It’s a non-standard coverage measure used when credit score has dried up as a result of banks is not going to lend to one another (out of the concern of counterparty default). It’s a final resort when merely reducing rates of interest is unlikely to realize the required end result. It was the Fed’s weapon of option to fight the credit score crunch that occurred in the course of the Nice Monetary Disaster in 2008. It entails the Fed printing extra {Dollars} and utilizing them to purchase US authorities bonds predominantly from monetary establishments. QE normally results in a weaker US Greenback.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse course of whereby the Federal Reserve stops shopping for bonds from monetary establishments and doesn’t reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It’s normally optimistic for the US Greenback.