AUD/JPY pulls again from intra-day highs at 96.65, regardless of the beneficial threat sentiment

- Aussie Greenback good points stay restricted under 96.65 and maintains an instantaneous bearish pattern in play.
- The Yen stays on the defensive, weighed by weaker demand for secure belongings after the US-Japan deal.
- The dovish RBA minutes and weak Australian information are appearing as headwinds for the AUD.
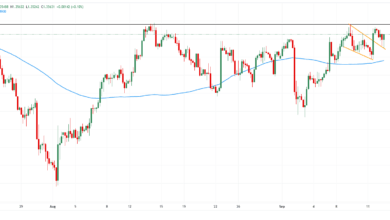
The Australian Greenback is without doubt one of the strongest performers in a risk-off session on Wednesday and is buying and selling greater towards the safe-haven Japanese Yen. The instant AUD/JPY pattern, nonetheless, stays bearish, in a sequence of decrease highs since peaking at 97.45 final week, and with bulls capped under 96.60 to date at the moment.
The Aussie rallied along with different risk-sensitive belongings throughout Wednesday’s Asian and European buying and selling classes, following US President Trump’s announcement of a commerce cope with Japan. This settlement has contributed to easing buyers’ fears in regards to the unsure outlook for world commerce and boosted hopes of extra such offers forward of the August 1 deadline.
The Yen picks up after PM Ishiba denies rumours of resignation
The Japanese Yen drew some assist within the Early European session as Japan’s Prime Minister Ishiba stepped as much as deny rumours unfold by native media, suggesting that he may resign by the top of August. Ishiba´s feedback have contributed to easing considerations about political uncertainty and have offered some assist to the JPY.
In Australia, the minutes of the July 7-8 assembly revealed that some committee members voted for a 25 bps price reduce, which heightened market expectations that the financial institution may ease its financial coverage additional after the August assembly, and elevated unfavourable strain on the pair.
On Wednesday, the Australian Westpac Main has failed to supply any important assist to the Aussie. The Index fell to 0.03% in June from the earlier month’s 0.1reading. These ranges level to a weak financial progress that provides causes for the RBA to proceed reducing charges subsequent month.
RBA FAQs
The Reserve Financial institution of Australia (RBA) units rates of interest and manages financial coverage for Australia. Selections are made by a board of governors at 11 conferences a yr and advert hoc emergency conferences as required. The RBA’s major mandate is to take care of value stability, which suggests an inflation price of 2-3%, but in addition “..to contribute to the steadiness of the foreign money, full employment, and the financial prosperity and welfare of the Australian individuals.” Its most important software for attaining that is by elevating or decreasing rates of interest. Comparatively excessive rates of interest will strengthen the Australian Greenback (AUD) and vice versa. Different RBA instruments embody quantitative easing and tightening.
Whereas inflation had at all times historically been regarded as a unfavourable issue for currencies because it lowers the worth of cash generally, the other has truly been the case in fashionable occasions with the relief of cross-border capital controls. Reasonably greater inflation now tends to guide central banks to place up their rates of interest, which in flip has the impact of attracting extra capital inflows from world buyers in search of a profitable place to maintain their cash. This will increase demand for the native foreign money, which within the case of Australia is the Aussie Greenback.
Macroeconomic information gauges the well being of an economic system and may have an effect on the worth of its foreign money. Traders choose to take a position their capital in economies which can be secure and rising somewhat than precarious and shrinking. Larger capital inflows enhance the combination demand and worth of the home foreign money. Basic indicators, similar to GDP, Manufacturing and Companies PMIs, employment, and shopper sentiment surveys can affect AUD. A robust economic system might encourage the Reserve Financial institution of Australia to place up rates of interest, additionally supporting AUD.
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a software utilized in excessive conditions when decreasing rates of interest will not be sufficient to revive the circulate of credit score within the economic system. QE is the method by which the Reserve Financial institution of Australia (RBA) prints Australian {Dollars} (AUD) for the aim of shopping for belongings – often authorities or company bonds – from monetary establishments, thereby offering them with much-needed liquidity. QE often ends in a weaker AUD.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It’s undertaken after QE when an financial restoration is underway and inflation begins rising. While in QE the Reserve Financial institution of Australia (RBA) purchases authorities and company bonds from monetary establishments to supply them with liquidity, in QT the RBA stops shopping for extra belongings, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It might be optimistic (or bullish) for the Australian Greenback.