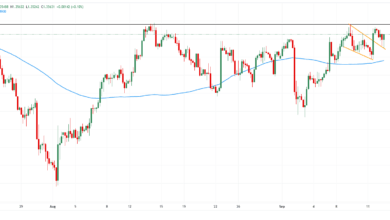
- AUD/JPY holds constructive floor to round 95.50 in Tuesday’s Asian session.
- The RBA unexpectedly holds its OCR regular at 3.85% on the July assembly.
- Trump stated Japan would face tariffs of 25% except it reached an settlement with the US.
The AUD/JPY cross gathers power to close 95.50 through the early Asian buying and selling hours on Tuesday. The Australian Greenback (AUD) attracts some consumers in opposition to the US Greenback (USD) after the Reserve Financial institution of Australia (RBA) rate of interest resolution.
The RBA board members determined to depart the Official Money Fee (OCR) unchanged at 3.85% at its July coverage assembly on Tuesday. The choice stunned the market expectations of a 25 foundation factors (bps) minimize to three.6%.
The RBA financial coverage assertion stated that the board can be attentive to the information and the evolving evaluation of dangers to information its choices, including that the outlook stays unsure. The eye will shift to the RBA press convention afterward Tuesday. Hawkish remarks from the RBA Governor may increase the Aussie, whereas a dovish message tends to weaken it.
On the JPY’s entrance, US President Donald Trump late Monday introduced imposing 25% levies on items from Japan, efficient August 1. Trump warned that any retaliatory tariff can be met with even greater tariffs however left the door open to reduction from the measures for nations that ease commerce obstacles.
Japanese Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba stated early Tuesday that Japan hasn’t been capable of attain an settlement with the US as a result of the nation saved defending what must be defended. Moreover, weak wage progress knowledge launched from Japan earlier may additional complicate the Financial institution of Japan’s (BoJ) path to normalizing financial coverage and become a key issue weighing on the JPY.
RBA FAQs
The Reserve Financial institution of Australia (RBA) units rates of interest and manages financial coverage for Australia. Choices are made by a board of governors at 11 conferences a 12 months and advert hoc emergency conferences as required. The RBA’s main mandate is to take care of value stability, which suggests an inflation fee of 2-3%, but additionally “..to contribute to the soundness of the foreign money, full employment, and the financial prosperity and welfare of the Australian individuals.” Its fundamental instrument for reaching that is by elevating or decreasing rates of interest. Comparatively excessive rates of interest will strengthen the Australian Greenback (AUD) and vice versa. Different RBA instruments embrace quantitative easing and tightening.
Whereas inflation had at all times historically been regarded as a destructive issue for currencies because it lowers the worth of cash normally, the other has truly been the case in trendy instances with the comfort of cross-border capital controls. Reasonably greater inflation now tends to guide central banks to place up their rates of interest, which in flip has the impact of attracting extra capital inflows from international buyers in search of a profitable place to maintain their cash. This will increase demand for the native foreign money, which within the case of Australia is the Aussie Greenback.
Macroeconomic knowledge gauges the well being of an financial system and might have an effect on the worth of its foreign money. Buyers desire to speculate their capital in economies which might be secure and rising fairly than precarious and shrinking. Better capital inflows improve the mixture demand and worth of the home foreign money. Traditional indicators, equivalent to GDP, Manufacturing and Companies PMIs, employment, and client sentiment surveys can affect AUD. A robust financial system might encourage the Reserve Financial institution of Australia to place up rates of interest, additionally supporting AUD.
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a instrument utilized in excessive conditions when decreasing rates of interest isn’t sufficient to revive the circulation of credit score within the financial system. QE is the method by which the Reserve Financial institution of Australia (RBA) prints Australian {Dollars} (AUD) for the aim of shopping for property – normally authorities or company bonds – from monetary establishments, thereby offering them with much-needed liquidity. QE normally ends in a weaker AUD.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It’s undertaken after QE when an financial restoration is underway and inflation begins rising. While in QE the Reserve Financial institution of Australia (RBA) purchases authorities and company bonds from monetary establishments to offer them with liquidity, in QT the RBA stops shopping for extra property, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It will be constructive (or bullish) for the Australian Greenback.