- The US Greenback is extending its reversal from $86.00 for the fourth day in a row.
- The tepid response to the US-China deal and traders’ warning forward of the US CPI are supporting the Rupee.
- USD/INR is approaching a key help space at 85.25-85.35.
The Indian Rupee is buying and selling larger for the fifth consecutive day on Wednesday. The US Greenback-supportive impression from the US-China deal has been short-lived, and the pair resumed its downward pattern forward of the US CPI launch, nearing the help space at 85.25-85.35.
US and China agreed on a framework to de-escalate their commerce rift and return to the Geneva assembly consensus, that’s, fewer restrictions for uncommon earths’ commerce and decrease tariffs. The shortage of particulars in regards to the settlement, nevertheless, has triggered a sceptical market response.
The Greenback ticked up after the information earlier than dropping floor in the course of the US Session, with traders cautious forward of the discharge of US CPI knowledge and a key public sale of US Treasury bonds due later as we speak.
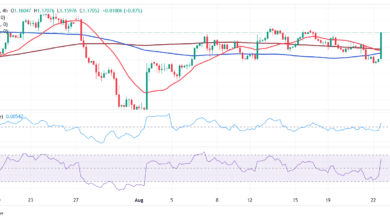
Technical evaluation: USD/INR bears stay in management
The USD/INR retains correcting decrease from the 86.00 peak hit final week, prone to lengthen losses in the direction of the important thing 85.25-85.35 space, the place the lows of Could 28 and 30 and June 2 meet the ascending trendline help from early Could lows.
The pair is transferring in an ascending triangle sample, which is a bullish formation, however technical indicators are pointing decrease, and the affirmation beneath the talked about ranges would enhance unfavorable stress in the direction of 84.77 (Could 26 and 27 lows), forward of the 12 Could low, at 84.25.
On the upside, a break above $86.00 to mark a pattern shift and set its focus in the direction of the April 9 excessive, at 86.90.
USD/INR 4-Hour Chart
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is without doubt one of the most delicate currencies to exterior components. The worth of Crude Oil (the nation is very depending on imported Oil), the worth of the US Greenback – most commerce is carried out in USD – and the extent of overseas funding, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Financial institution of India (RBI) in FX markets to maintain the alternate price secure, in addition to the extent of rates of interest set by the RBI, are additional main influencing components on the Rupee.
The Reserve Financial institution of India (RBI) actively intervenes in foreign exchange markets to take care of a secure alternate price, to assist facilitate commerce. As well as, the RBI tries to take care of the inflation price at its 4% goal by adjusting rates of interest. Larger rates of interest normally strengthen the Rupee. That is because of the function of the ‘carry commerce’ during which traders borrow in nations with decrease rates of interest in order to put their cash in nations’ providing comparatively larger rates of interest and revenue from the distinction.
Macroeconomic components that affect the worth of the Rupee embody inflation, rates of interest, the financial development price (GDP), the stability of commerce, and inflows from overseas funding. A better development price can result in extra abroad funding, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A much less unfavorable stability of commerce will finally result in a stronger Rupee. Larger rates of interest, particularly actual charges (rates of interest much less inflation) are additionally optimistic for the Rupee. A risk-on surroundings can result in better inflows of International Direct and Oblique Funding (FDI and FII), which additionally profit the Rupee.
Larger inflation, notably, whether it is comparatively larger than India’s friends, is mostly unfavorable for the forex because it displays devaluation via oversupply. Inflation additionally will increase the price of exports, resulting in extra Rupees being offered to buy overseas imports, which is Rupee-negative. On the identical time, larger inflation normally results in the Reserve Financial institution of India (RBI) elevating rates of interest and this may be optimistic for the Rupee, as a consequence of elevated demand from worldwide traders. The alternative impact is true of decrease inflation.