- The US Greenback is regaining misplaced floor as commerce struggle fears ease.
- Swiss CPI contracted in Could, which nearly confirms an SNB minimize in June.
- Later immediately, US Manufacturing unit Orders and Job Opening figures may problem the USD’s restoration.
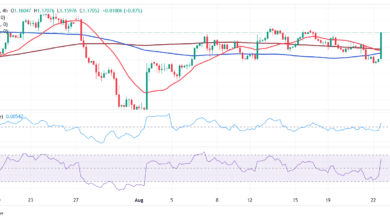
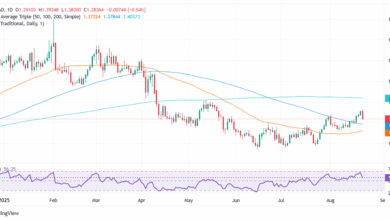
The US Greenback is posting average positive factors on Tuesday’s European session, reaching intra-day highs previous the 0.8200 psychological stage, after bouncing up from at 0.8155, six-week lows. Easing issues about commerce wars are supporting the US Greenback’s restoration, and weighing on the safe-haven Swiss Franc.
In Switzerland, Could’s Client Costs Index fell to deflation ranges for the primary time since 2021. The month-to-month CPI ticked up 0.1% after a flat studying, as anticipated, however yearly inflation contracted 0.1%, cementing hopes that the SNB will minimize its benchmark charge to zero at its June assembly.
Within the US, knowledge from Monday confirmed that the tariff uncertainty is taking its toll on the manufacturing sector. The ISM Manufacturing PMI eased to 48.3 in Could from 48.8 in April in opposition to market expectations of a rise to 49.5. The ISM report additionally highlighted longer supply instances, spurring issues about potential shortages in some merchandise.
The market will likely be attentive to April´s Manufacturing unit Orders immediately for a extra correct evaluation of Trump’s “Liberation Day” in manufacturing facility exercise. New orders are anticipated to have fallen at a 3% charge within the month, following a 3.4% enhance within the earlier month. The chance is skewed to the draw back for the USDollar.
Other than that, US JOLTS Job Openings are anticipated to indicate that demand for employment remained pretty regular, with 7.1 million openings in April, after the 7.19 million seen within the earlier month. These figures will body Wednesday’s ADP report and Friday’s Nonfarm Payrolls launch. The Greenback would wish sturdy employment figures to ease issues from manufacturing facility knowledge.
SNB FAQs
The Swiss Nationwide Financial institution (SNB) is the nation’s central financial institution. As an impartial central financial institution, its mandate is to make sure worth stability within the medium and long run. To make sure worth stability, the SNB goals to take care of applicable financial circumstances, that are decided by the rate of interest stage and trade charges. For the SNB, worth stability means an increase within the Swiss Client Worth Index (CPI) of lower than 2% per 12 months.
The Swiss Nationwide Financial institution (SNB) Governing Board decides the suitable stage of its coverage charge in keeping with its worth stability goal. When inflation is above goal or forecasted to be above goal within the foreseeable future, the financial institution will try and tame extreme worth progress by elevating its coverage charge. Greater rates of interest are typically constructive for the Swiss Franc (CHF) as they result in larger yields, making the nation a extra enticing place for traders. Quite the opposite, decrease rates of interest are likely to weaken CHF.
Sure. The Swiss Nationwide Financial institution (SNB) has frequently intervened within the international trade market with the intention to keep away from the Swiss Franc (CHF) appreciating an excessive amount of in opposition to different currencies. A robust CHF hurts the competitiveness of the nation’s highly effective export sector. Between 2011 and 2015, the SNB applied a peg to the Euro to restrict the CHF advance in opposition to it. The financial institution intervenes out there utilizing its hefty international trade reserves, often by shopping for foreign exchange such because the US Greenback or the Euro. Throughout episodes of excessive inflation, significantly resulting from vitality, the SNB refrains from intervening markets as a powerful CHF makes vitality imports cheaper, cushioning the worth shock for Swiss households and companies.
The SNB meets as soon as 1 / 4 – in March, June, September and December – to conduct its financial coverage evaluation. Every of those assessments ends in a financial coverage choice and the publication of a medium-term inflation forecast.